View Metadata Map
Language Variants
Género de publicación; Veröffentlichungsgenre; Publicatie genre; Julkaisun lajityyppi.
Usage Notes
Genre is often used in academic accounts interchangeably with type and format, although these terms can also be used to specify sub-divisions such as broadsheet versus quarto. Genre can also refer to periodicity and frequency, and distinct types such as family papers, police gazettes and society papers. The term genre was not commonly used in this sense in the nineteenth century.
In Trove, there are some journals that have found their way into the newspaper digitisation project owing to practicalities at the time of digitisation. Publications such as government gazettes, which are technically journals, were digitised with the newspapers because they did not have the process for journals at the time. Similarly, publications that changed genre (such as The Bulletin, which started as a newspaper but became a magazine) are listed under the first genre for the run.
Examples:
At the broadest level (newspaper, periodical, magazine)
“the periodical as a publishing genre“ has sustained a remarkable development since the 18th century.” [Beetham, 96]
“The second example points out the interdependence of various publishing genres in the periodical marketplace, emphasizing how this informed the reputations of editors and contributors.” [Tilley, 210]
“A newspaper can change its form and content to become a periodical. Do not make a new record to reflect a change in format from newspaper to periodical (or vice versa). Instead, give the information in a note. In the case of a newspaper that has changed to a periodical, leave the Type of Serial (008/21) code as ‘n.’ Existing subject headings should retain their form subdivisions with a change in format, and additional headings may be input to reflect the new format.” [Sagendorf and Moore, 42]
“Young Ireland responded quickly to political events, and the newspaper format, with its cheapness and topicality, was crucial to the success of the movement.” [Tilley, 210]
As a sub-category of journalism
“Although it seems a commonplace, the nineteenth-century press is characterized by a number of distinct genres beyond that of the usual distinction between periodicals and newspapers.” [DNCJ, LRB, 245]
“The Journal was inserted into the market as a ‘cheap illustrated miscellany’, and to understand the expectations this aroused in the implied reader, it is necessary to sketch a history of the genre.“ [King 2004, 49]
“Journalistic genres such as news articles, editorial comment, foreign correspondence, political debate, court reports, financial bulletins, illustrations, sports coverage and even advertisements…” [Nicholson 2012, 277]
“Tiettyä lajityyppiä ohjaavat tietyt säännönmukaisuudet.”
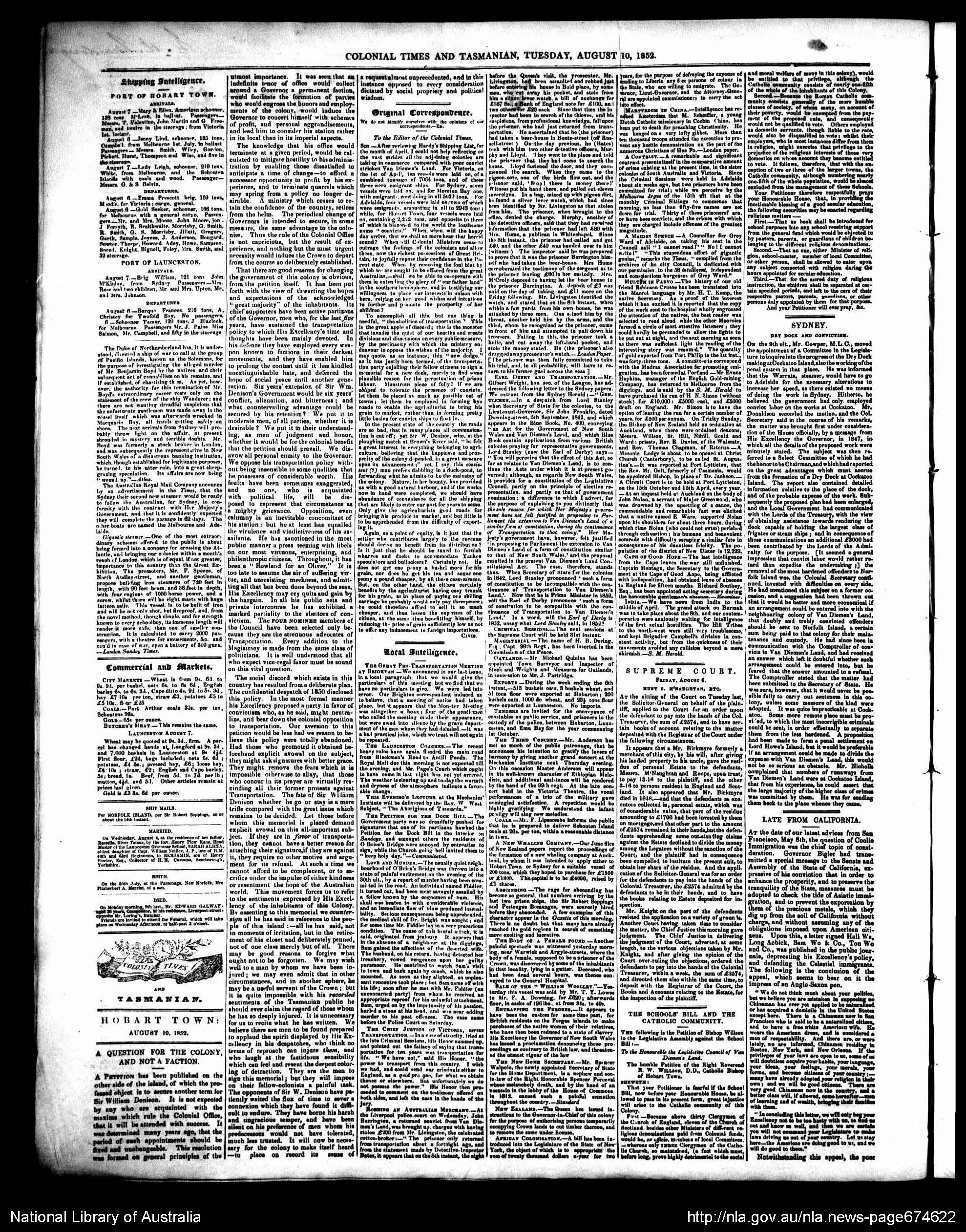
Example showing departments including Shipping Intelligence, Commercial and Markets, Ship Mails, Married, Birth, Died, Original Correspondence, Local Intelligence, Supreme Court and Sydney, from Colonial Times, 10 August 1852: 2. Trove.